What Is CBL?
Challenge-Based Learning (CBL) is an educational approach where students engage in real-life, (multi)disciplinary, socio-technical and/or scientific challenges. These challenges are ill-structured and open-ended, lacking a singular "right" solution. These challenges are ideally presented by societal or industry stakeholders and require the development or proposal of a solution.
For the development of the solution, the acquisition, integration and transfer of scientific knowledge from various disciplines alongside the application of transversal skills like critical thinking and problem-solving is needed. The learning process in CBL is active, self-directed, collaborative, and encourages students to become comfortable with uncertainty.
CBL as Educational Concept
Based on the work of the CBL Taskforce we use the following 10 dimensions to define Challenge Based Learning at TU/e (van den Beemt, et al., 2022).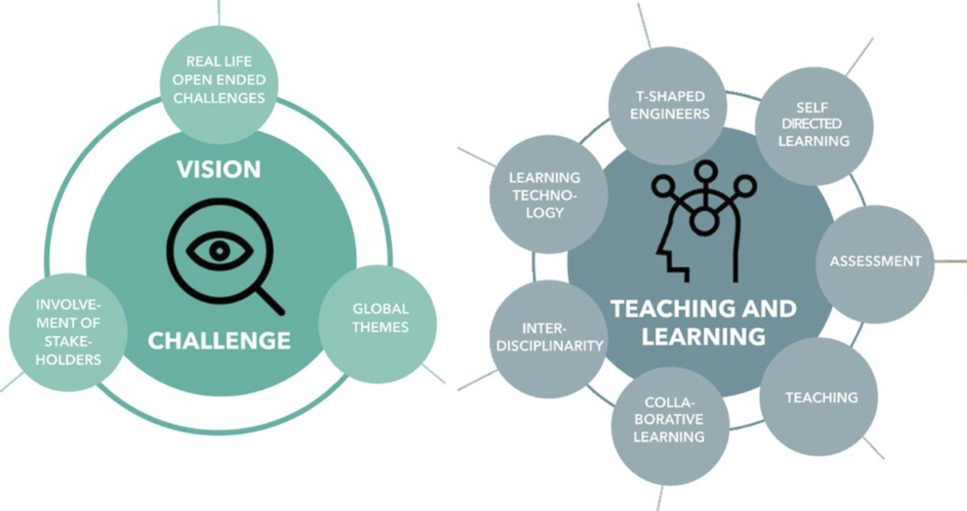
The CBL dimensions provide a structured framework for understanding and implementing CBL effectively. We use these dimensions for analyzing the variety of CBL implementations, to show how CBL can be tailored to fit different curricula, phases of a study program and student types. The educational concept of CBL is incorporated within the curriculum and expressed in CBL courses and CBL projects. What are the differences between these two levels? Find out below.
CBL on Course Level
CBL courses are available within the curriculum in the core program and in the elective space. TU/e also offers extracurricular CBL projects that students can attend via innovation Space and EWUU.
CBL courses and projects are designed by educators, supported by Teacher Support. A CBL course has an open-ended, real-life challenge as the basis of student learning. This challenge must be solved by a team in which they collectively explore and define the problem in detail. Then the team develops and presents an appropriate approach and proposal for a solution.
The work process is supportive of the learning process so that every student gets as much as possible out of the learning experience. Therefore, good learning activities, assessment and feedback methods are needed to support learning. The dimensions of CBL (in the CBL Compass/Aspiration Wheel) help to take all these characteristics into account when shaping CBL on a course level.
CBL on Curriculum Level
As an educational concept CBL is more than just a course. It can manifest in various forms within our university's educational landscape. At a curriculum level, CBL signifies the successful implementation and integration of CBL courses with other curricular elements within bachelor or master programs.
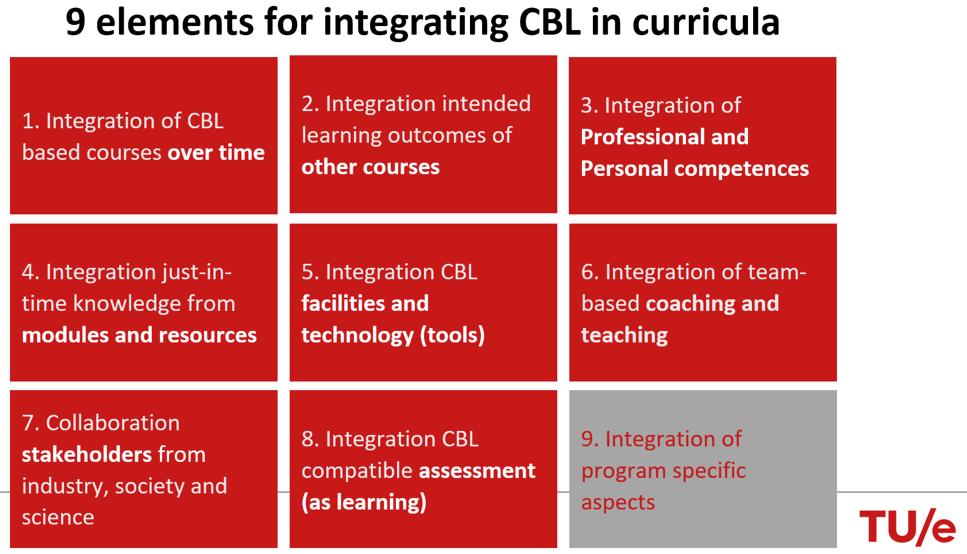
The Taskforce has identified 9 elements (now referred to as building blocks) that serve as guidelines for integrating CBL with other aspects of a curriculum. While the 10 dimensions help shape CBL on a course level, these 9 elements aid curriculum designers to integrate CBL into the curriculum. Below is an initial elaboration of each element.
We initiated element 1 in 2023, ensuring that all bachelor programs include at least one CBL based course every semester. This sequence of mandatory CBL courses, increasing in complexity, forms what is known as a CBL curriculum line. Thereafter, CBL will be implemented in the master's programs within the Graduate School. Stay tuned to this page for regular updates.