Sociophysics 1, 2 and 3 - 3QAUS0
About this course
- Lecturers: Federico Toschi (responsible educator), Antal Haans, Gunter Bombaerts.
- Academic level: Bachelor Q3, elective
- Number of students: 90
- Number of ECTS: 5
- Disciplines: Applied Physics and Science Education, Applied Physics and Science Education
- Status: The course was last taught in 2023, after which its contents and learning objectives were partially moved to other CBL courses in the curriculum.
- Topic: This course is about Sociophysics, using mathematical tools inspired by physics to understand the behavior of human crowds, either online (e.g. on social platforms, stock exchanges) or physically (e.g. the case of crowd dynamics in a railway station). The course is part of the USE Learning Line “Physics of Social Systems” (made of Sociophysics 1, 2 and 3)
Set-up
The USE Learning line “Physics of Social Systems” is composed by 3 courses:

In this learning line students work in the same groups throught 3 courses. Students received data from stakeholders and in some cases use the Market Hall Living Lab to carry out experiments. The key essence of CBL education in this USE Learning Line is that student teams create their own challenge and define their project by identifying appropriate Guiding Questions, Guiding Activities and Guiding Resources. Additionally, student groups work according to the SCRUM methodology in the following way:
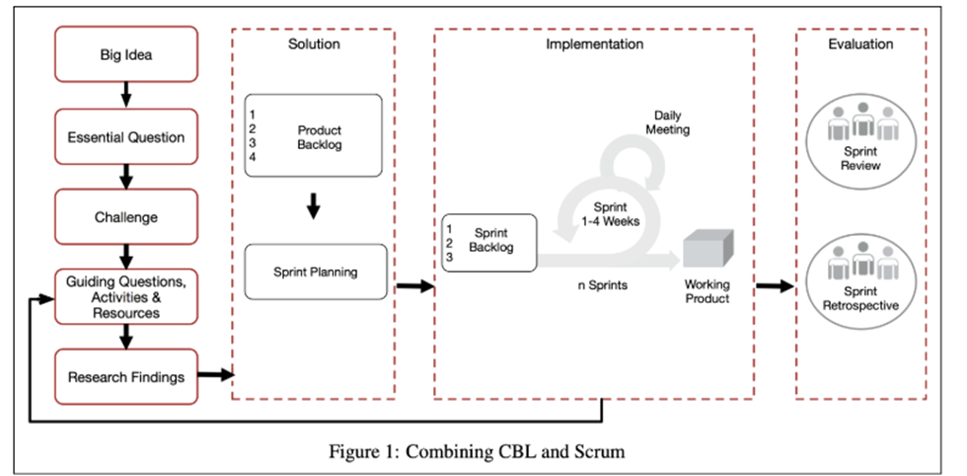
Figure 1: Combining CBL and Scrum. Reproduced from Santos, A. R., Sales, A., Fernandes, P., & Nichols, M. (2015, June). Combining challenge-based learning and scrum framework for mobile application development. In Proceedings of the 2015 ACM conference on innovation and technology in computer science education (pp. 189-194).
The course uses a self-developed dashboard to track students’ progress and output and to provide feedback to them.
Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO’s)
- You understand the physics and psychology necessary to quantitatively describe and model the behavior of social systems.
- You understand and are able to explain the ethical implication of performing research with human subjects.
- You can apply concepts from mathematics physics and psychology to interpret social systems behaviour.
- You can combine mathematical, physics and psychology concepts and tool-kits for analyzing, studying and modelling social systems.
- You can meaningfully reflect on your analyses and models.
- You can create a new, integrated and multidisciplinary approach to model and nudge social systems.
- You can create (design and conduct) an experiment to validate and extend the models and nudging protocols developed in course 2.
- You get an informed insight into how social systems can be quantitatively analyzed and modeled in in practice.
- You can apply the concepts to refine the setup of your research project.
- You can apply the different disciplinary knowledge by effectively collaborating in groups.
- You can communicate your ideas about how to observe, model and nudge social systems in a global context to a diverse set of stakeholders.
Assessment
This course used the following methods of assessment:
- Group Poster Presentation (weight 15%) – peer grading amongst groups
- Group report (weight 60%) – graded by lecturers
- Peer evaluation of the group work (weight 10%) – per grading within the group
- Group presentation to stakeholder(s) and lecturer(s) (weight 15%) – graded by lecturers and stakeholders
Go to thhe rubric for the poster presentation to find out how the presentations are assessed.
Learning progress was tracked by a self-developed dashboard. This dashboard allowed the teachers to:
- Give (real-time) feedback on guiding guiding questions (GQs), guiding activities (GAs) and guiding resources (GRs) with a grade (1 to 5 stars); this allows student group to rapidly converge on the definition of their own project;
- visualize graphs showing the average scores (quality of both CBL and Scrum performances);
- (formative) peer-grade each other on a weekly basis;
- have the TAs review their teams’ performance within Scrum each week;
- peer-grade posters at the end of the course;
- collect all grades.
Learning Activities
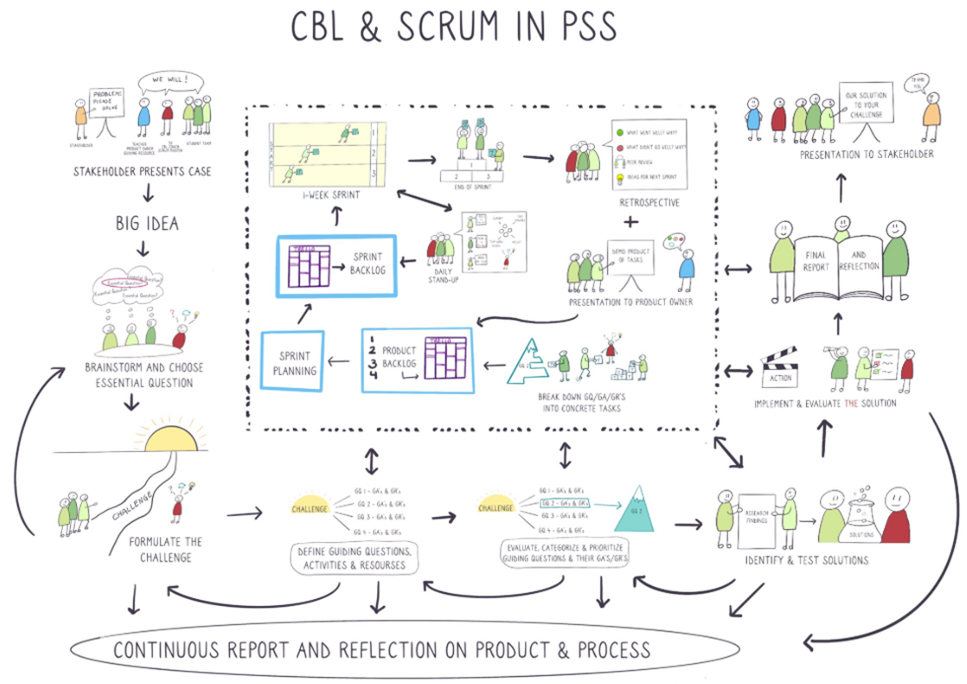
The course incorporates two core aspects, namely Challenge Based Learning (CBL) and Scrum. CBL constitutes a learning experience and teaching method incorporating complex and real-world problems, whereas Scrum is a project management framework. See the corresponding modules for more information.
The USE Learning Line starts with a bootcamp week, in which students tackle a challenge about litter on campus. During this week students become familiar with Challenge-Based Learning, Scrum AND will help the Stakeholder solve their problem.
During the first two weeks, lectures and key information are provided. Among others, this includes explanations regarding the core aspects of the course (CBL and SCRUM), an explanation of the approach, the schedule, and the deliverables.
Furthermore, in week 1, key aspects of CBL are defined. Specifically, the Stakeholder(s) provide inspiration for the Big Idea(s). During weeks 1 and 2, student groups start working in order to go from the Big Idea to the Essential Question and The Challenge and start defining their Guiding Questions, Guiding Activities, and Guiding Resources.
During weeks 3 to 8, the student groups start working on their projects (The Challenge), according to the principle of Scrum. This means that student groups (Scrum teams) work in weekly sprints and hold daily Scrum meetings, under the coaching of teaching assistants (Scrum masters), towards the continuous development and refinement of their final products (group presentation, group poster, group report).
The course schedule consists of weekly working slots, it is synthetically summarised in the Syllabus but more extensively detailed and explained on the Schedule page.
Finally, students are advised to regularly check announcements for the latest news.
Organisation of the course
- Teaching Assistants (TAs) tutored the students on a weekly basis. The TAs followed their own specific training program.
- The teachers reviewed the students' work on a weekly basis. Each group of students was assigned to one of the 5 teachers who guided their output throughout the process.
- The stakeholder presented the big idea and attended the intermediate and final (poster) presentations.
More information
- Please visit the TU/e Living Labs page for more information and to find out how to use Living Labs in your course.
- You can visit the Dashboard page yourself. If you’d like to get a better picture of it or find out if it’s useful for your course, please contact Federico directly.

